issue 128 | 30 aug 2025
The integrity flash
Analysis of Developments in the Space Domain
in this issue
Kings on the Move: China Maneuvers 3x TJS Satellites
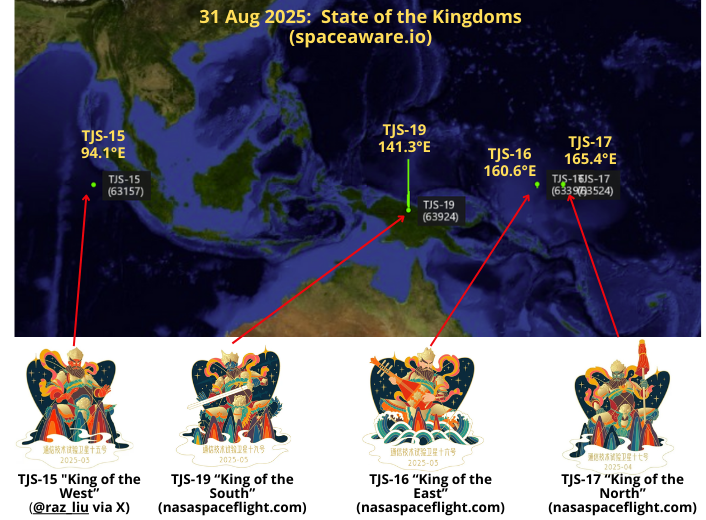
23 Aug 2025: China repositioned three of its four “King” satellites. TJS-15 (King of the West) (63157), TJS-16 (King of the East) (63397), and TJS-17 (King of the North) (63524) all have maneuvered eastward and have assumed new positions in the GEO belt. Only TJS-19 (King of the South) (63924) has yet to maneuver. The mission of these satellites remains unknown. China announced all four had the identical mission and would be “mainly used to verify multi-band and high-speed satellite communication technology.”
-Background:
- TJS-15 launched 7 Mar 2025 on LM-3B to 90.3°E
- TJS-16 launched 29 Mar 2025 on LM-7A to 152.50°E
- TJS-17 launched 10 Apr 2025 on LM-3B to 152.74°E
- Note separation of only 0.24° east (171 km) of TJS-16
- TJS-19 launched 12 May 2025 on LM-3C to 141.3°E
Editor’s note: China launched more TJS satellites in the first 6 months of 2025 (5) than in any other year.
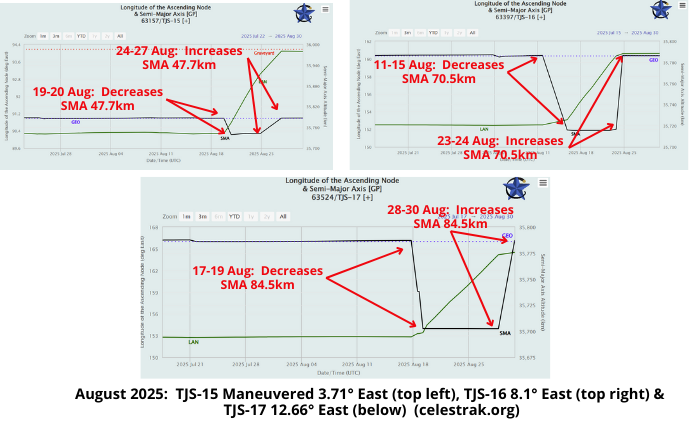
– Maneuver Summary:
- TJS-15: Moved East 3.71°
- 14-15 July decreased inclination 0.2° (to 0.0°)
- 19-20 Aug decreased SMA 47.7km and initiated 0.57°/day eastward drift.
- 27 Aug increased SMA 44.8 km and parked at 94.09°E
- At its new location TJS-15 will be in the vicinity of USA 315 (SBRIS GEO 5 (48618)). On 29 Aug at 0500Z the two had POCA ~95km.
- TJS-16: Moved East 8.1°
- 11-15 Aug: Decreased SMA 70.5km and initiated 0.91°/day eastward drift.
- 24 Aug: Increased SMA ~70.5km rejoins the GEO belt at 160.6°E.
- TJS-17: Moved East 12.66°
- 17-19 Aug: decreased SMA 84.5km and initiated 1.1°/day eastward drift.
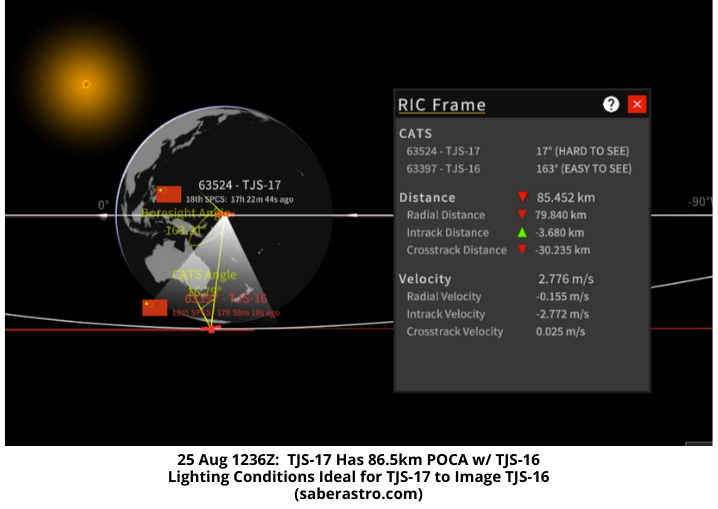
- 25 Aug: 1236Z, passed TJS-16 (China originally placed the two satellites near one another) and had a point of closest approach of ~86km. Lighting conditions at POCA were ideal for TJS-17 to image TJS-16. (graphic)
- 29 Aug: TJS-17 increased SMA 84.5km rejoins the GEO belt at 165.4°E
- TJS-19 has yet to conduct significant maneuvers and remains at 141.3°E.
China Conducts 2 Launches Adds 14 Guowang Satellites
17 Aug 2025: China launched a Long March-6A from Taiyuan with the ninth group of SatNet LEO satellites (SatNet LEO Group 09) (65228-65232) for the Guowang constellation. China launched the satellites into a co-planar orbit with the 5 satellites from Group 4. LM-6A Launch.
25 Aug 2025: China launched a Long March-8A from Wenchang with the tenth group of SatNet LEO satellites (SatNet LEO Group 10) for the Guowang constellation. The LM-8A carried 9 satellites (65305-65313) into a 50° inclined orbit. Launch Video.
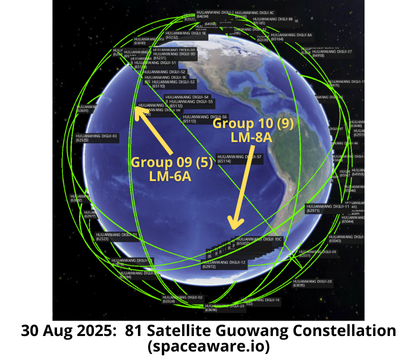
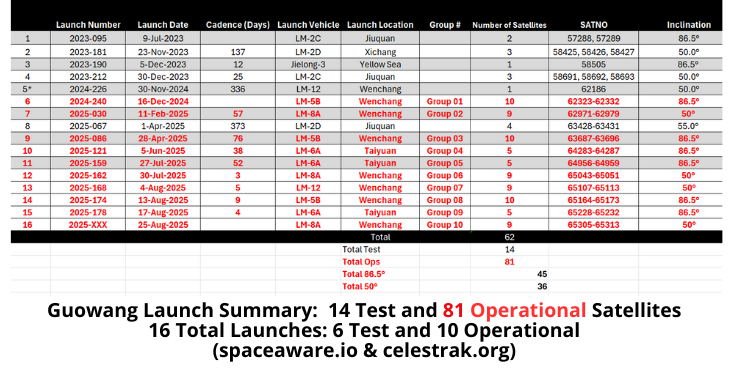
– With this launch there are now 81 satellites in the operational Guowang constellation (see graphics & tables). Additionally, China has launched 14 Guowang test satellites.
– China launched Group 9 into a co-planar orbit with Group 4. There are now 10 satellites in this particular plane.
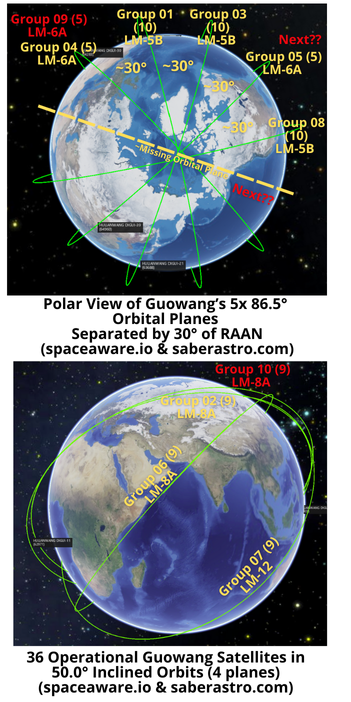
– China is building out the Guowang constellation with orbits inclined either 50.0° or 86.5°. Currently there are 36 satellites in 4 50.0° orbital planes and 45 satellites in 5 86.5° orbital planes.
– Summary of Guowang Operational Launches
- Group 1 (16 Dec 2024): 10 sats on LM-5B. Orbit inclined 86.5°
- Group 2 (11 Feb 2025): 9 sats on LM-8A. Orbit inclined 50.0°
- Group 3 (28 Apr 2025): 10 sats on LM-5B. Orbit inclined 86.5°
- Group 4 (5 Jun 2025): 5 sats on LM-6A. Orbit inclined 86.5°
- Group 5 (27 Jul 2025): 5 sats on LM-6A. Orbit inclined 86.5°
- Group 6 (30 Jul 2025): 9 sats on LM-8A. Orbit inclined 50.0°
- Group 7 (4 Aug 2025): 9 sats on LM-12. Orbit inclined 50.0°.
- Group 8 (13 Aug 2025): 10 sats on LM-5B. Orbit inclined 86.5°
- Group 9 (17 Aug 2025): 5 sats on LM-6A. Orbit inclined 86.5° (co-planar with Group 4)
- Group 10 (25 Aug 2025): 9 sats on LM-8A. Orbit inclined 50.0°.
– Observations
- For the 86.5° inclined orbits (Groups 01, 03, 04, 08 & 09) the target SMA appears to be 1,167.9km. It appears the intended RAAN separation is ~30° between planes.
- Group 09’s 5 satellites are co-planar with the 5 Group 04 satellites. China’s initial deployment appears to be 10 satellites per 86.5° orbital plane. Expect the next 86.5° launch to head to the remaining open plane or augment the Group 05 satellites. (see graphic)
- The 50° orbits do not appear to have a standard operating altitude. Group 2 settled at 1,149.3km, Group 6 appears to have settled at 880km (no change in 3 weeks) and Group 7 may have settled at 901km (no change in 5 days). Will continue to monitor.
– Deployment Status (all data as of 30 Aug 2025)
- 86.5° Orbits (target SMA 1,167.9km)
- Group 1 reached operating altitude in 109 days.
- Group 3 reached operating altitude in 37 days.
- Group 4 satellites reached ~1,095+km and continue to raise their SMAs.
- Group 5 satellites reached ~1,075km and continue to raise their SMAs.
- Group 8 satellites reached ~1,120km and continue to raise their SMAs.
- Group 9 satellites started at an altitude of ~1,002km and are now at ~1,012km and continue to raise their SMAs.
- 50.0° inclined orbits (multiple target SMAs?)
- Group 2 reached operating altitude of 1,149.3km in 77 days
- Group 6 reached ~880km and are no longer raising their SMAs. This may be their operational altitude (achieved after 16 days).
- Group 7 reached ~901km and are no longer raising their SMAs. This may be their operational altitude (achieved after 21 days.)
- Group 10 started at an altitude of ~873km and are now increasing their SMAs.
China: Launches SY-28B 02 Into Unusual Orbit
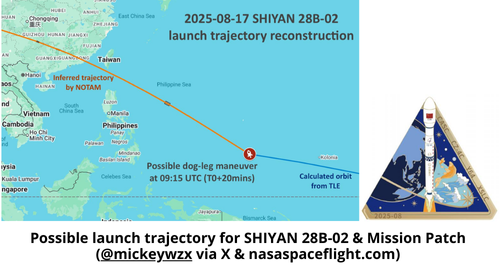
17 Aug 2025: Nearly six weeks after launching Shiyan-28B 01 (64753) China launched Shiyan-28B 02 (65226) on a Long March-4C launch vehicle from Xichang. According to official sources, the satellite entered the desired orbit and “will be mainly used for space environment exploration and related technology tests”. Both SY-28 spacecraft are in an unusually low inclination (11°) which was a first for China. To reach this inclination from Xichang requires China to conduct a “dog-leg” maneuver with the LM-4C as it headed to orbit. Launch Video.
– China’s mission description of the Shiyan-28B satellites exactly matched that of the 6 Shiyan-27A-F (63599-63604) China launched into a sun-synchronous orbit on 18 Apr 2025.
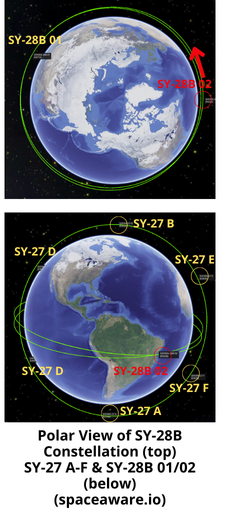
– SY-28B 02 is not co-planar with SY-28B 01 as their is a RAAN difference of ~33°. Both satellites are inclined 11° and orbiting at an average altitude of ~795km. They are orbiting on opposite sides of the Earth, ensuring that when one satellite is over the western hemisphere the other is over the eastern hemisphere.
-The 6 SY-27 satellites are nearly evenly spaced in their 99.7° inclined orbit and have an average altitude of 1,049.5km.
21 Aug 2025: Russia launched its 5th Angara-1.2 launch vehicle from Plesetsk. On board were multiple military spacecraft which were successfully delivered to low earth orbit (LEO). Russia’s Ministry of Defense released little/no information regarding the satellites, however there is evidence that the Angara delivered four OO MKA imagery satellites (65267-65270) into a 334 x 317km, 96.6° inclined sun-synchronous orbit (SSO). Launch Video.
– As usual, Bart Hendrickx had the best information regarding this launch. Per Bart’s post on nasaspaceflight.com:
- “Apparently these satellites are of the same type as Kosmos-2577 and 2578, launched by Angara-1.2 in September last year. Earlier satellites belonging to this series would seem to have been Kosmos-2551 (Soyuz-2.1v), Kosmos-2555 (Angara-1.2), Kosmos-2560 (Angara-1.2), Kosmos-2568 (Soyuz-2.1v), Kosmos-2574 (Soyuz-2.1v) and Kosmos-2575 (Soyuz-2.1v).”
- “Early versions were called ‘EO MKA’ and later ones ‘OO MKA…’ EO and OO denote different phases in the research phase of a project, with OO being closer to the operational version.”
- “The four new satellites…expand the coverage of the constellation. They are in an orbital plane separated by about 40° from that of Kosmos-2578 (Kosmos-2577 never maneuvered and re-entered last February, most likely due to an on-board failure).”
- “Kosmos-2578’s orbital plane in turn is only about 4° from that of Kosmos-2574 and 2575. The orbits of Kosmos-2575 and 2578 are being phased to ensure that they pass over the same general region on Earth with an interval of roughly 45 minutes.”
- “The four satellites were released in pairs with a certain interval. This suggests that they were stacked two by two on top of each other, which is also confirmed by the fact that Angara-1.2 used its standard payload fairing for this launch…the satellites now seem to have reached a level of maturity that has given the Russians enough confidence to launch four of them in one go. With Angara-1.2 having a maximum payload capacity to Sun-synchronous orbit of 2.4 tons, the individual mass of the satellites should not exceed 600 kg.”
- “If the four new satellites mimic the behavior of their maneuverable predecessors, their orbits will initially decay to about 300 km before they start making orbit corrections. These are most likely made with an electric propulsion system.”
- “There can be little doubt that these satellites are on some type of optical reconnaissance mission…the high launch rate is a clear sign that it has been given high priority by the Ministry of Defense.”

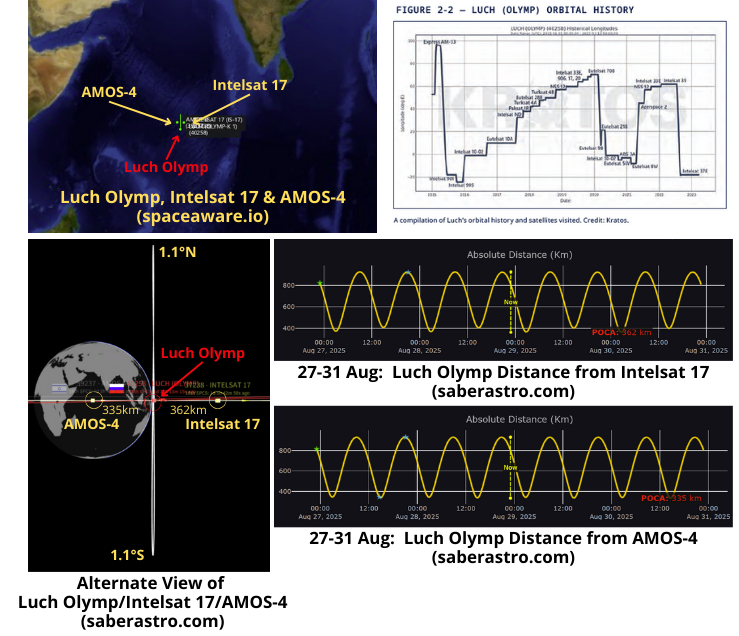
Russia: Luch Olymp Maneuvers & Finds a New Home
28 Aug 2025: After drifting eastward for 150 days, Russia’s Luch Olymp (40258), a suspected SIGINT collection satellite, has found a new home…and new neighbors. From 11-24 Aug Russian satellite operators increased the Luch Olymp’s SMA 51.7km to rejoin the GEO belt at 65.5°E (south-southwest of India) longitude. Luch Olymp’s new neighbors are Intelsat 17 (37238) and AMOS-4 (29237); both are communications satellites. Russia has positioned Luch Olymp nearly exactly between Intelsat 17 and AMOS-4. This is normal behavior for Luch Olymp, the satellite has shifted its location on the GEO belt several times. Luch Olymp’s previous neighborhood was off the west coast of Africa where it was orbiting “near” Intelsat 37E (42950). You can find a great summary of its activities in the latest edition of the Secure World Foundation’s “Global Counterspace Capabilities” document (published by friend of the Flash Victoria Samson!) Specifically pages 2-11 through 2-13 (see graph below from 2023).
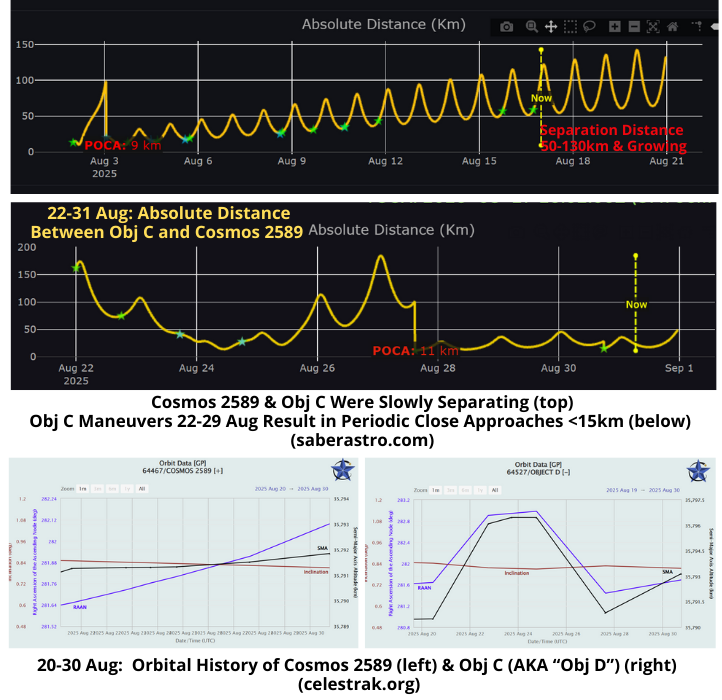
Russia: Object C Renews RPO with Cosmos 2589
20-27 August 2025: In the 17 Aug Flash I reported Obj C (64527) had maneuvered and was no longer in RPO conditions with Cosmos 2589 (64467). Between 20-27 Aug Russian space operators made several small maneuvers resulting in Obj C resuming RPO with Cosmos 2589. While it is difficult to know for certain, it appears Obj C made the majority of the maneuvers.